By Admin – Steroidal.com
It has long been claimed that drinking green tea can aid in longevity amongst other positive health benefits, drinking various teas has been suggested by nutritionist and doctors for decades. As well as being a potent anti-oxidant green tea can actually make you live longer. According to a new study conducted by Harbin Medical University in China and soon to be published in Ageing Cell, animals that consumed 300mg of EGCG every day lived 14% longer than those that didn’t.
Teas contain a number of flavonoids, but green tea in particular contains catechins such as epicatechin-gallate [ECG], epigallocatechin-gallate [EGCG] and catechin, epigallocatechin [EGC]. EGCG has long been touted as the key ingredient in extending life expectancy by researchers and is also a key ingredient in fat loss dietary supplements.
Recent review articles suggest that substances like EGCG inhibit the activity of free radicals and inflammatory proteins such as TNF-alpha. [Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2012;88(3):88-101.] As we get older and age, our sensitivity inflammatory proteins and free radicals, such as, TNF-alpha become more pronounced and active causing excessive damage compared to adolescent years. Due to this the chances of crucial molecules and cells becoming damaged increases, thus enhancing our chances of developing cancers, diabetes and other health problems.
According to a 2001 study, the average Dutchman consumes 50 mg catechins daily from drinking tea. [Eur J Clin Nutr. 2001 Feb;55(2):76-81.] The Chinese then converted this level of consumption to an equivalent dosage for rats, and arrived at 5 mg EGCG per kg bodyweight per day. The conversion was done using skin surface area and not bodyweight, which is often confused. For simplicity’s sake they also assumed that catechins and EGCG were interchangeable.
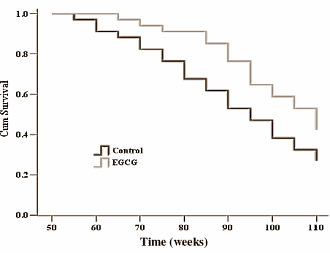
The researchers started by giving the animals 5mg/kg per day of EGCG and nothing was observed. They then increased this dosage by factor 5 and results were seen. Crucially, rats given 25mg/kg of EGCG lived 2 months longer than those in the control group.
Rates not given EGCG lived an average of 92.5 weeks, compared to those that were given 25mg/kg of EGCG lived 105 weeks, which is 14% longer.
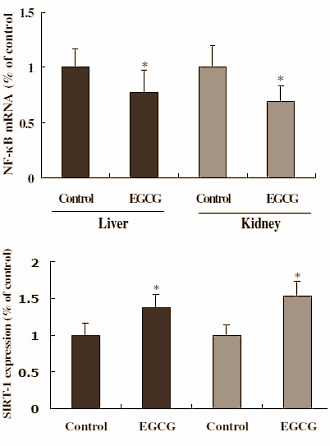
Other key points were that the EGCG had no effect on the rats insulin levels or blood pressure. Blood analysis of the rats liver and kidneys showed that they had healthier organs compared to the control group. The EGCG rats also weighed slightly less than those given no EGCG.
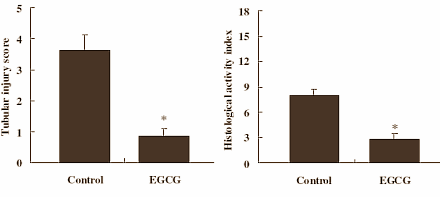
The Chinese measured the histological activity index for the liver and the tubular injury score for the kidneys. The higher the scores, the worse the condition of the rat’s liver and kidneys. The scores for the tissues in the EGCG rats were significantly lower than those of the tissues in the control group.
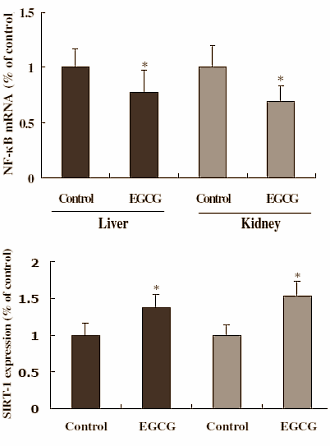
The Chinese then concluded that the EGCG aided the longevity of the rats, by maintaining liver and kidney health by inhibiting TNF-alpha and activating SIRT1. “Our study suggests that long-term consumption of phytochemicals with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities could be beneficial in promoting health and extending lifespan”, they concluded.
An 80kg human’s comparable dosage of EGCG is around 320mg every day. These amounts can be found in over the counter dietary supplements.
Source:
Aging Cell. 2013 Jul 8. doi: 10.1111/acel.12133. [Epub ahead of print].